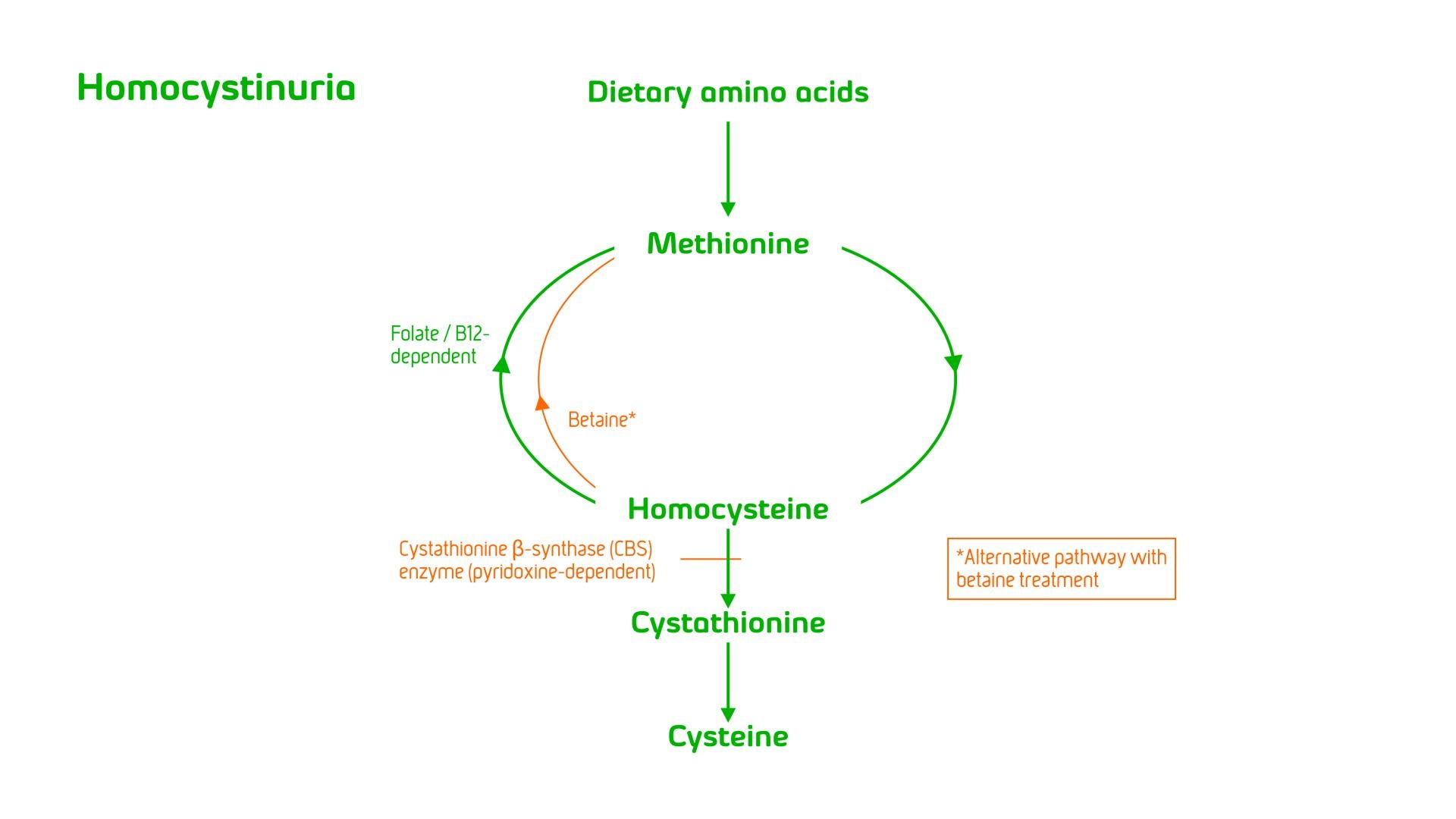
Homocystinuria (HCys) is a rare metabolic disorder resulting from the deficiency of cystathionine beta-synthase which (along with vitamin B6) is involved in the conversion of homocysteine to cystathionine. A deficiency of this enzyme leads to accumulation of homocysteine and its precursor, methionine in body fluids.
HCys is an autosomal-recessive disorder, with prevalence between 1 in 1,800 and 1 in 900,000.
The disease shows a wide range of severity and can potentially affect many different organs of the body. The four organ systems most commonly involved are eye, skeleton, brain and vascular system.
Patients with HCys may have dislocation of the lens (the most characteristic finding occurring between 2 and12 years of age), varying degrees of mental retardation, skeletal abnormalities and vascular problems including thromboembolism and ischaemic strokes.
Prompt detection and treatment of HCys are important in preventing or reducing the symptoms associated with the disorder.
The disease can be diagnosed by determination of the plasma total homocysteine level in affected individuals or by newborn screening.
Treatment aims to prevent complications by lowering plasma homocysteine concentration, and avoidance of abnormally low methionine concentration. Some patients respond to therapy with pyridoxine (vitamin B6). The dietary management consists of a methionine restricted diet with betaine supplementation.
comida-HCys A formula is an amino acid mixture, free from methionine, supplemented with vitamins, minerals and trace elements, and provides energy from fat and carbohydrates appropriate to the different age groups.

