Urea cycle disorders (UCDs) are a group of metabolic diseases, which are caused by the deficiency of one of the six enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are involved in biochemical reactions in which nitrogen, a waste product of protein metabolism, is changed to urea and removed from blood.
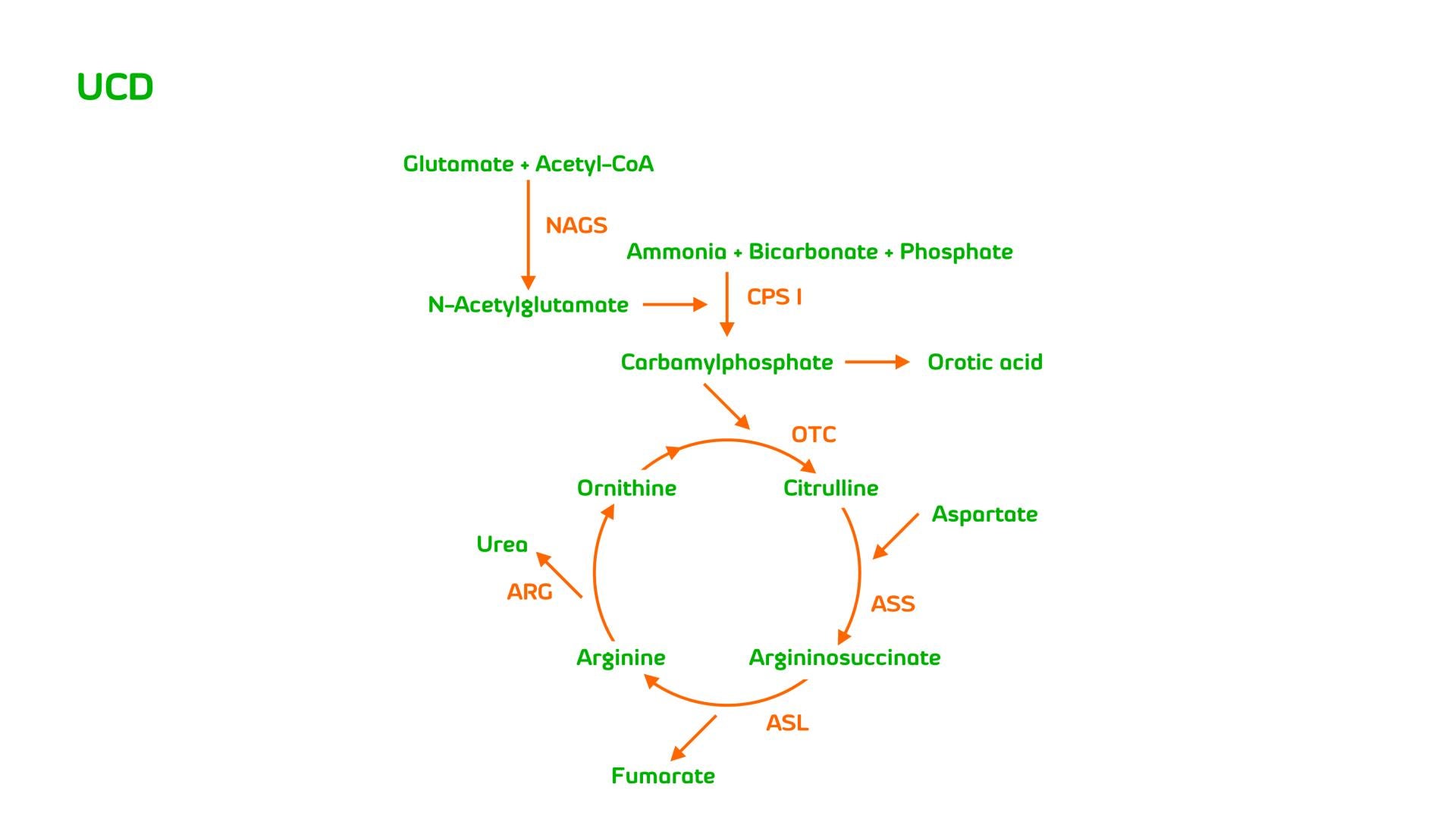
Without the proper enzymes, the process cannot be completed and nitrogen accumulates in the blood in the form of ammonia, a highly toxic substance. Untreated, the high amounts of ammonia can cause brain damage, coma and death.
Urea cycle disorders occur in about 1 in 8,000 to 44,000 births.
The presentation of symptoms may occur at birth or later in life, and may differ among affected individuals in severity, depending on the gene mutation that caused the condition.
Symptoms may include: irritability, poor feeding, vomiting, drowsiness and, in severe cases, coma. In children with mild or moderate UCD who do not show symptoms until early childhood, symptoms may include: disliking meat or other foods rich in protein, vomiting, nausea, mental confusion or hyperactive behaviour, fatigue, weakness and drowsiness.
Treatment is a lifelong process and the main aim is to keep the level of ammonia in the blood down at safe levels.
The treatment involves: dietary protein restriction, medications, amino acid supplements, liver transplantation.
The comida-UrC product line consists of mixtures of essential amino acids, enriched with L-Cystine and L-Tyrosine, and is supplemented with vitamins, minerals and trace elements relevant for different age groups.

